- Industries & Machines Industries & Machines
- IIoT IIoT
- Service-Toll Processing Service-Toll Processing
- Material Material
- News News
- IR Information IR Information
-
Sustainability
Sustainability
Sustainability
- Introduction
- Hosokawa Micron Group "Basic Human Rights Policy"
- Hosokawa Micron Group "Basic Policy on the Environment"
- Sustaibality Policy - Mission Statement
- Editorial Policy
- Integrated Report
- Materiality & Strategy
- Technological contribution to a sustainable global environment
- Contributions towards a safer, more secure and prosperous society
- Sophistication of governance that supports business
- ESG Data Collection
- Sustainable Business Management ~ Finance
- Infromation Disclosure Based on TCFD Recommendations
- Jobs and Careers Jobs and Careers
-
About Us
About Us
About Us
- Greetings (Company Introduction)
- Hosokawa Micron Group "Basic Human Rights Policy"
- Hosokawa Micron Group "Basic Policy on the Environment"
- Management Philosophy
- Corporate Overview
- Executive Officers
- Corporate Profile
- Business Areas and Strengths
- Corporate History
- Hosokawa Micron Group
- Domestic Facilities
- Overseas Subsidiaries (Asia)
- Overseas Subsidiaries (Europe)
- Overseas Subsidiaries (America)
- Asian Agents
- Powder Technology Research Institute
- Industrial Property Rights
- Journals and Books
- Technical Information
- Annual Publication "Micromeritics"
- Compliance Charter
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Quality Principle

Industries & Machines
- TOP
- Industries & Machines
- Industries Search
- Dental Ceramic
Dental Ceramic

Summary
As the dental materials, metal and plastic have been used traditionally. However, the use of ceramics is increased because of its excellent biocompatibility and aesthetics. Modern dental ceramics should not only be inherently stable and durable, but should also be easy to handle for the dental technician. Required end-product fineness values depend on the application and the mixture, and range from 10 to 30 µm.
Contents

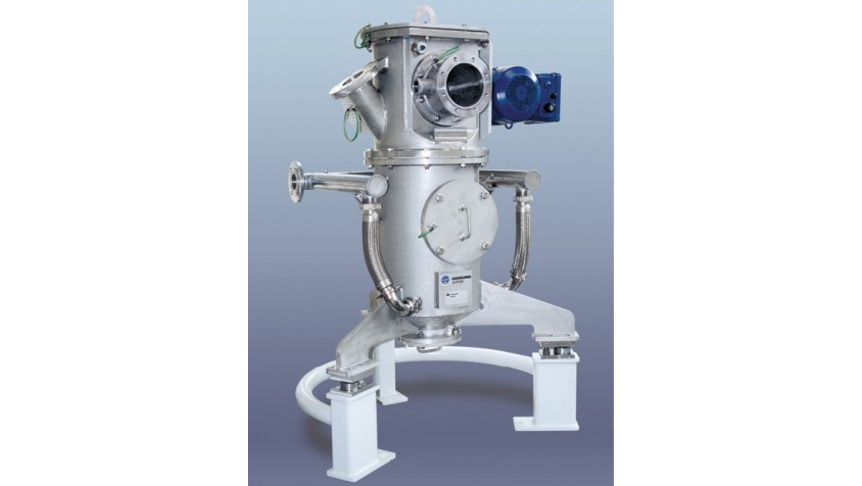
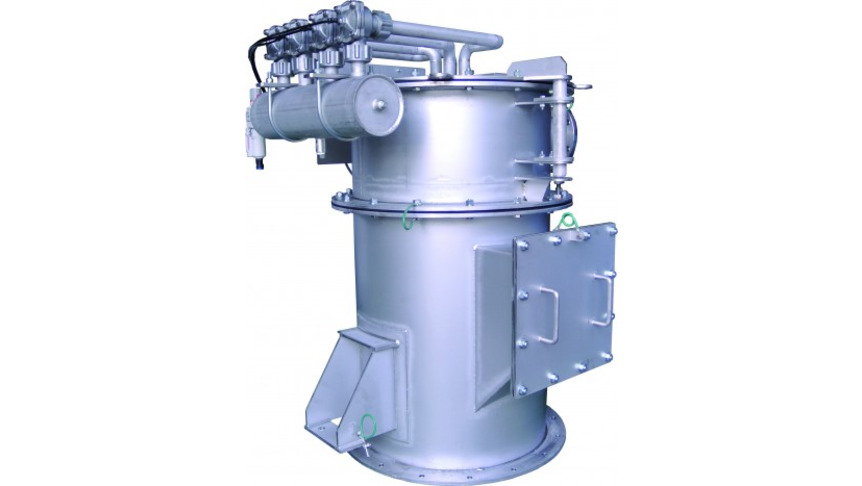
Fig.1 Fluidized bed opposed jet mill 400AFG
The traditional process of manufacturing ultrafine powder mixtures with a batch ball mill is time-consuming and the results are not always reproducible. Fluidized bed opposed jet mills have become widespread because of the continuous operating mode at exact compliance with the end-product fineness and reproducible process conditions.
After being sintered, the material is usually pre-crushed and sometimes also pre-ground with a ball mill to 500 µm. We are the expert in the comminution of a great variety of different dental compounds, including alumina ceramic, zirconia ceramic as well as silicate ceramic. Filling compounds and dental or phosphate cement are also included in this field.
Contamination
Besides keeping to the demanded particle size distribution, contamination of the mixture with ferrous particles must be prevented by all means. And this is where the many years of cooperation with customers from the hard materials comminution sector bear fruit. The low-contamination technology of jet milling in a fluidized bed has established itself as the ideal process solution for dental compounds. We offer selected lining materials for the various system components. Besides engineering ceramics, polymer materials or coatings are used in the product-contact zone.
Composing
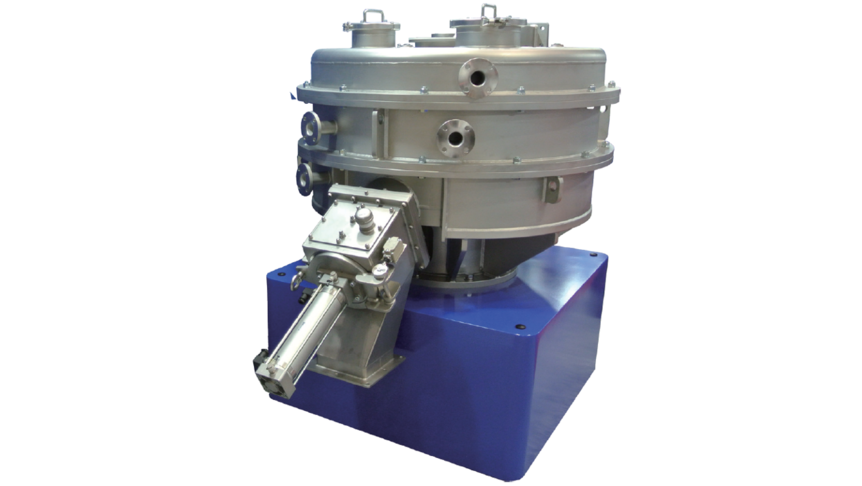
Jet milled ceramics powder shows the average size of a few micron meters. This fine powder is highly cohesive and adhesive, and difficult to mix/disperse by ordinary dry mixer. By loading higher shear force than the cohesive force, possible to coat fine ceramics on the surface of core particles (Fig.2). For this precision mixing/composing purpose, Nobilta (Fig.4) is the most applicable. Nobilta principle is to load high impact/shear/compression force on particles resulting with intensive mixing, coating and composing for R&D work in dental ceramic material.
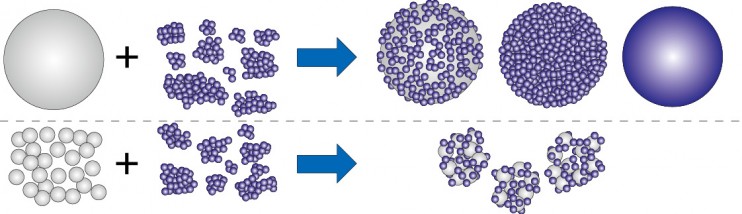
Fig.2 Schematic figure of composing
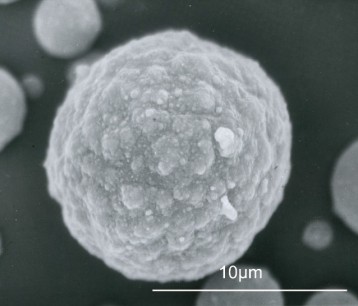
Fig.3 Ceramic composite particle

Fig.4 Nobilta NOB-130
Related equipments

Feel free to contact us. if you have any questions or concerns.






